真实案例研究
梅奥诊所佛罗里达州成像增强智能中心
在临床影像工作流程中集成和部署 AI 模型

将成像相关(基于像素和非像素)的人工智能 (AI) 模型有效集成到现有临床放射科工作流程中至关重要,因为这些添加内容可能会极大地影响(正面或负面)操作效率或下游决策制定(例如,手术、病理学、介入治疗和药物注意事项)[1]。为了促进影像 AI 能力的无缝集成,同时尽量减少对现有放射科工作流程的负面影响(图 1),梅奥诊所佛罗里达州的成像增强智能中心 (CAII) 开发了与 MONAI [2] 软件包(例如,“MONAI Core”和“MONAI Deploy”)功能兼容的基础设施和模块化软件包。

基于 AI 的基础设施应该与现有 IT 环境无异,并且最多只需要对放射科用户(例如,放射科医生和技术员)进行最少的培训。尽管如此,引入此类工具需要培养用户和受益者(例如,患者和转诊临床医生)之间的信任。
作为在医学领域应用 AI 的主导学科,放射科已经认识到需要在影像 AI 应用的各个方面提高效率,包括 AI 模型:开发、部署以及适应实际应用场景。不幸的是,这些过程仍然耗时、费力且成本高昂,往往严重限制了有意义的影像 AI 应用(图 2)。

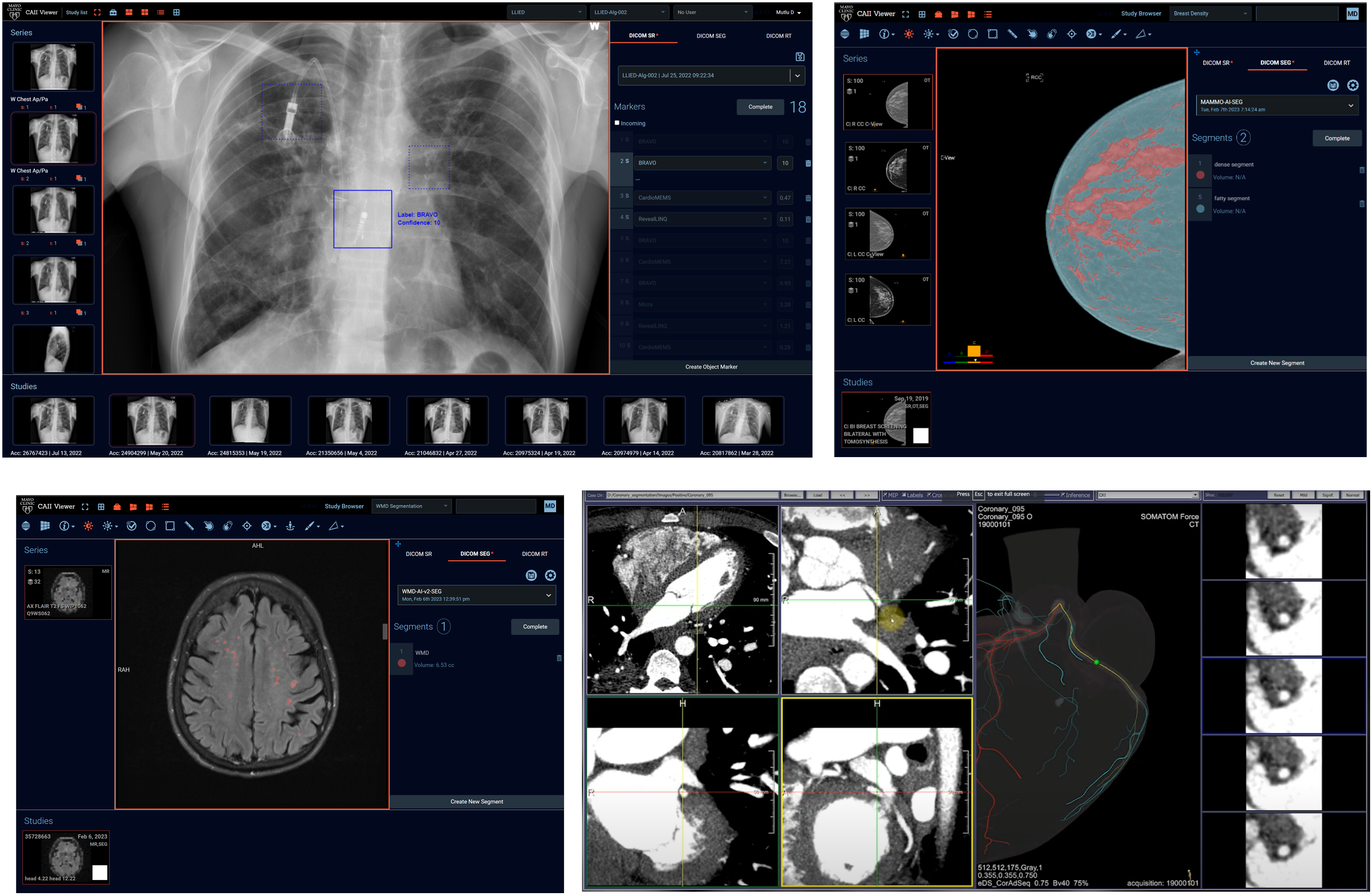
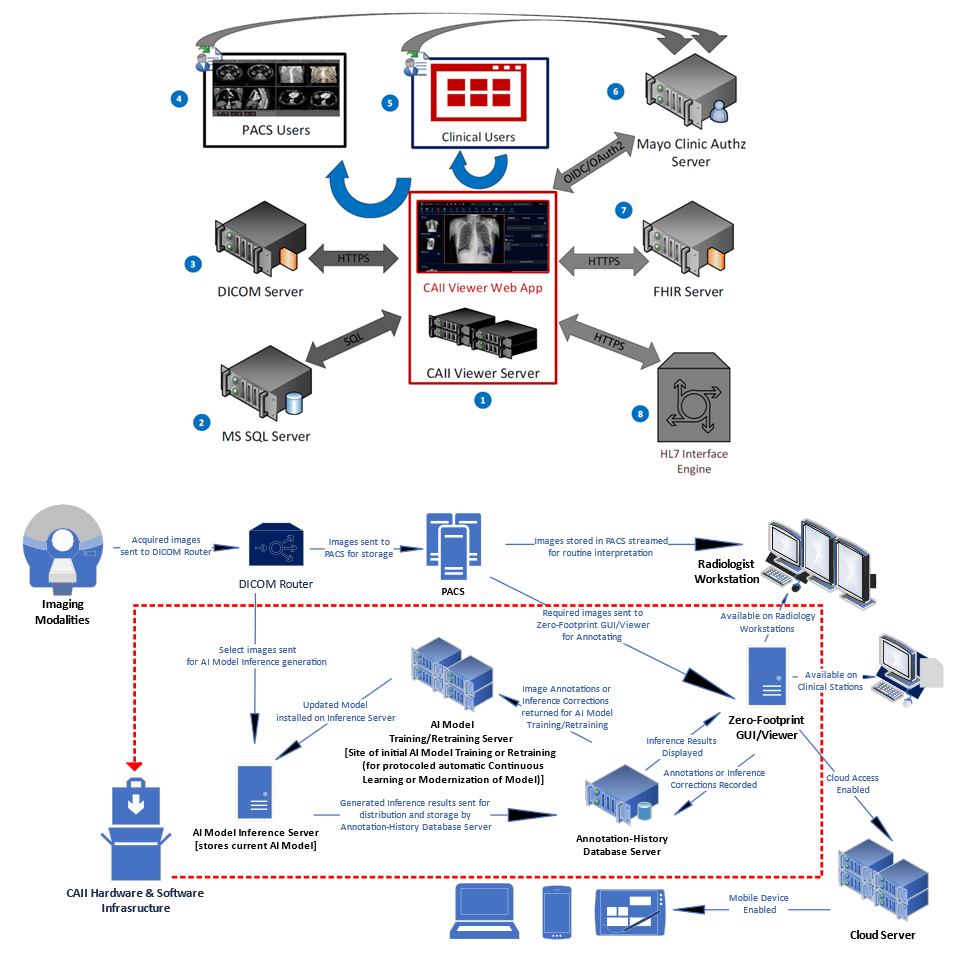
在 CAII 工作的工程师、影像科学家和医生开发了基础设施和容器化软件包,使影像 AI 模型能够无缝集成到繁忙的放射科现有 IT 环境中 [3-9]。必要的接口和软件包(图 3)可以部署在本地、云端或混合环境中(图 4)。目标是要求最少的用户培训和 IT 支持,并增强用户和受益者的信心。
梅奥诊所佛罗里达州的 CAII 开发了多种功能,以简化影像 AI 模型与放射科工作流程的集成。这些功能包括
- 危急结果警报
- 专家参与循环的 AI 模型部署
- 临床环境下的按需模型训练
- 临床环境下的实时用户推理结果裁定及反馈
- 用户满意度监测
- 用于 FDA 批准的数据收集
- 持续学习
- 联邦学习
- 临床系统之间的基于标准的通信(DICOM、FHIR、HL7、IHE)
- 关于系统和模型性能的基于标准的数据收集
参考文献
- 1. Gupta V, Erdal BS, Ramirez C, Floca R, Jackson L, Genereaux B, Bryson S et al. "Current State of Community-Driven Radiological AI Deployment in Medical Imaging." arXiv preprint arXiv:2212.14177 (2022).
- 2. Cardoso J, Li W, Brown R, Ma N, Kerfoot E, Wang Y, Murrey B et al. "MONAI: An open-source framework for deep learning in healthcare." arXiv preprint arXiv:2211.02701 (2022).
- 3. Testagrose C, Gupta V, Erdal BS, White RD, Maxwell RW, Liu X, Kahanda I, Elfayoumy S, Klostermeyer W, Demirer M. "Impact of Concatenation of Digital Craniocaudal Mammography Images on a Deep-Learning Breast-Density Classifier Using Inception-V3 and ViT." In 2022 IEEE International Conference on Bioinformatics and Biomedicine (BIBM), pp. 3399-3406. IEEE, 2022.
- 4. White RD, Demirer M, Gupta V, Sebro RA, Kusumoto FM, Erdal BS. "Pre-deployment assessment of an AI model to assist radiologists in chest X-ray detection and identification of lead-less implanted electronic devices for pre-MRI safety screening: realized implementation needs and proposed operational solutions." Journal of Medical Imaging 9, no. 5 (2022): 054504.
- 5. Gupta V, Demirer M, Maxwell RW, White RD, Erdal BS "A multi-reconstruction study of breast density estimation using Deep Learning." arXiv preprint arXiv:2202.08238 (2022).
- 6. Demirer M, White RD, Gupta V, Sebro RA, Erdal BS. "Cascading neural network methodology for artificial intelligence-assisted radiographic detection and classification of lead-less implanted electronic devices within the chest." arXiv preprint arXiv:2108.11954 (2021).
- 7. White RD, Erdal BS, Demirer M, Gupta V, Bigelow MT, Dikici E, Candemir S, Galizia MS, Carpenter JL, O'Donnell TP, Halabi AH, Prevedello LM. Artificial Intelligence to Assist in Exclusion of Coronary Atherosclerosis During CCTA Evaluation of Chest Pain in the Emergency Department: Preparing an Application for Real-world Use. J Digit Imaging. 2021 Jun;34(3):554-571. doi: 10.1007/s10278-021-00441-6. Epub 2021 Mar 31. PMID: 33791909; PMCID: PMC8329136.
- 8. Rockenbach MABC, Buch V, Gupta V, Kotecha GK, Laur O, Erdal BS, Yang D, Xu D, Ghoshajra BB, Flores MG, Dayan I, Roth H, White RD. Automatic detection of decreased ejection fraction and left ventricular hypertrophy on 4D cardiac CTA: Use of artificial intelligence with transfer learning to facilitate multi-site operations. ntelligence-Based Medicine. 2022; 6.
- 9. Gupta V, Taylor C, Bonnet S, Prevedello LM, Hawley J, White RD, Flores MG, Erdal BS. Deep Learning Based Automatic Detection of Adequately Positioned Mammograms. Lecture Notes in Computer Science: Domain Adaptation and Representation Transfer, and Affordable Healthcare and AI for Resource Diverse Global Health. 2021; 12968:239-250.